Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder that can manifest with a variety of symptoms. Due to the diverse nature of these symptoms, early diagnosis is crucial. Doctors typically use clinical symptoms and a range of tests to aid in the diagnosis. Below are the main methods for understanding hormonal changes and ovarian conditions through tests:
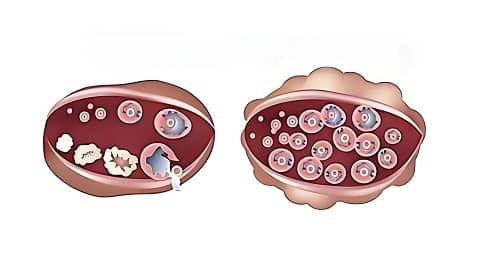
Table of Contents
- 1. Ultrasound: Key Indicator of Ovarian Morphology
- 2. Hormonal Level Testing: Identifying Hormonal Imbalance
- 3. Blood Sugar and Insulin Testing: Checking for Insulin Resistance
- 4. Other Tests: Excluding Other Causes
1. Ultrasound: Key Indicator of Ovarian Morphology
Ultrasound is an important tool for diagnosing PCOS. It helps doctors examine whether multiple small cysts are present in the ovaries, a common feature of PCOS. Typically, the ovaries of PCOS patients appear polycystic, and may show incomplete follicle development.
- Impact: Detects multiple cysts in the ovaries, aiding in the diagnosis of PCOS.
- Mechanism: The presence of multiple small cysts suggests impaired follicle development, disrupting normal ovulation.
2. Hormonal Level Testing: Identifying Hormonal Imbalance
PCOS patients often experience hormonal imbalances, particularly in the ratio of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) to FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone). Typically, LH levels are higher, and FSH levels are lower, resulting in an elevated LH/FSH ratio, which disrupts normal ovulation. Additionally, male hormones (such as testosterone) are usually elevated, leading to symptoms like hirsutism and acne.
- Impact: May cause irregular ovulation, affecting menstrual cycles and fertility.
- Mechanism: Hormonal imbalances affect ovarian function and interfere with ovulation.
3. Blood Sugar and Insulin Testing: Checking for Insulin Resistance
Many PCOS patients experience insulin resistance, meaning the body has a reduced response to insulin, leading to higher insulin levels. This not only interferes with other hormones but can also contribute to weight gain. By testing blood sugar and insulin levels, doctors can assess whether insulin resistance is present, helping to manage related health issues.
- Impact: Leads to weight gain, difficulty losing weight, and metabolic disturbances.
- Mechanism: Insulin resistance affects metabolism and promotes fat storage, leading to obesity.
4. Other Tests: Excluding Other Causes
Although ultrasound and hormonal testing are the main diagnostic tools for PCOS, doctors may recommend additional tests to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as thyroid dysfunction or other endocrine disorders.
- Impact: Helps exclude other possible causes and ensures an accurate diagnosis.
- Mechanism: Comprehensive testing ensures the correct identification of the underlying condition, preventing misdiagnosis.
Early Recognition and Management
The symptoms of PCOS can vary from person to person. Early recognition of these symptoms and timely intervention can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is recommended to seek medical advice for a professional diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Proper management can help restore health and hormonal balance.