Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants and begins to develop outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tubes, ovaries, or abdominal cavity. If not diagnosed and treated promptly, ectopic pregnancy can lead to severe health complications. Understanding the causes of ectopic pregnancy is crucial for prevention and early detection.
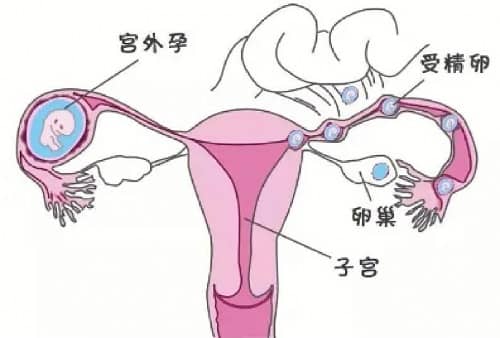
Table of Contents
- Fallopian Tube Issues
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Reproductive Structural Abnormalities
- Impact of Assisted Reproductive Technologies
- Unhealthy Lifestyle Habits
1. Fallopian Tube Issues
The fallopian tubes are the critical pathways through which the egg travels from the ovaries to the uterus. If there are any issues with the fallopian tubes, such as blockages or scarring, the fertilized egg may not be able to reach the uterus and may instead implant in the fallopian tubes, leading to an ectopic pregnancy. Common issues include:
- Fallopian Tube Infections: Infections, such as those caused by sexually transmitted diseases (e.g., gonorrhea or chlamydia), can lead to inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes, narrowing or blocking the tubes and preventing the egg from reaching the uterus.
- Previous Fallopian Tube Surgery: Any surgical damage to the fallopian tubes, such as due to previous surgeries or sterilization procedures, can also increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Damage to the fallopian tubes significantly increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy as the fertilized egg is unable to pass through the tubes properly and may implant along the way.
2. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones play a vital role in pregnancy. If there are any imbalances in key hormones such as progesterone or estrogen, it can interfere with the function of the fallopian tubes or the uterine lining, making it difficult for the fertilized egg to reach the uterus. For instance:
- Insufficient Progesterone: A lack of progesterone can prevent the uterine lining from being prepared to accept the embryo, or it may cause abnormal contractions in the fallopian tubes, which could impede the embryo’s movement to the uterus and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Estrogen Imbalances: Excess or insufficient estrogen levels can impact the motility of the fallopian tubes, affecting the transportation of the fertilized egg and raising the likelihood of ectopic implantation.
Hormonal imbalance is a significant risk factor for ectopic pregnancy as it disrupts the natural process of embryo transportation and implantation.
3. Reproductive Structural Abnormalities
Certain structural abnormalities in the reproductive organs can also contribute to ectopic pregnancy:
- Uterine Fibroids: These non-cancerous growths in the uterus can affect the structure of the uterus and hinder the normal implantation of the fertilized egg.
- Adenomyosis: This condition occurs when the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows into the uterine muscle, which may interfere with the implantation process.
- Congenital Uterine Anomalies: Abnormalities such as a septate uterus or an undeveloped fallopian tube can disrupt the normal passage of the fertilized egg to the uterus and lead to ectopic pregnancy.
- Endometrial Polyps: These growths in the lining of the uterus can obstruct the fertilized egg’s path, preventing it from properly implanting in the uterus.
These structural issues can block the fertilized egg’s passage through the fallopian tubes, causing it to implant in an abnormal location, leading to ectopic pregnancy.
4. Impact of Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Women undergoing assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), may have an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy. Factors contributing to this include:
- Embryo Implantation Failure: Sometimes, embryos that are transferred during IVF may not implant in the uterus but may instead remain in the fallopian tubes or other locations, resulting in ectopic pregnancy.
- Multiple Pregnancies: ART treatments, especially IVF, often increase the chances of multiple pregnancies, which can elevate the likelihood of ectopic implantation.
Women undergoing ART treatments need regular monitoring to ensure that the pregnancy is developing properly inside the uterus and to detect any potential ectopic pregnancies early.
5. Unhealthy Lifestyle Habits
Certain unhealthy lifestyle choices can contribute to the risk of ectopic pregnancy:
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol intake negatively affect reproductive health, causing issues such as fallopian tube damage and hormonal imbalances, which can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Overweight or Underweight: Both extremes of body weight—being either overweight or underweight—can interfere with normal reproductive function and affect the transportation of the fertilized egg, raising the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Poor Nutrition: A poor diet can lead to nutritional deficiencies and hormonal imbalances, which may hinder normal pregnancy processes and increase the chances of ectopic pregnancy.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and avoiding smoking and excessive drinking, is crucial for minimizing the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Conclusion
There are multiple causes for ectopic pregnancy, including fallopian tube issues, hormonal imbalances, reproductive abnormalities, assisted reproductive technologies, and unhealthy lifestyle habits. Understanding these causes and taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of ectopic pregnancy. If you experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, or other concerning signs, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly for diagnosis and treatment. Early detection and appropriate care are key to managing ectopic pregnancy and protecting your health.